Ecommerce has transformed the way businesses sell. But shipping products to global customers comes with its own set of challenges.
Product returns in particular tend to be a logistical nightmare. The reasons for a return vary widely. Statista estimates that 81% of returns are due to damage, 75% are due to improper fit, and 56% are due to an item not matching the product description.
Reverse logistics handles these returns. It encompasses everything from a customer’s decision to return the product to it arriving back at your warehouse and into sellable inventory.
With 16.5% of items eventually making their way back to the retailer, it’ll come as no surprise to hear that the global reverse logistics market is estimated to be worth $821.55 billion by 2025.
So, how does your brand manage a constant wave of product returns? This guide shares how to make the returns process easier for customers and your online store with reverse logistics.
What is reverse logistics?
Reverse logistics is the process of returning a product from the customer to the original point of origin.
If a customer is returning a t-shirt they ordered from your ecommerce store, for example, reverse logistics would bring the unwanted inventory back to your store or warehouse to be resold, reused, recycled, or refurbished.
It’s not just ecommerce returns that need a robust reverse logistics strategy. Any item making its way back to your warehouse needs to be tracked and handled appropriately, including:
-
Rented products
-
Items with delivery failures
-
Unsold inventory from third-party retailers and distributors (including products that have reached the end of their shelf life)
Reverse logistics vs. traditional logistics
Traditional ecommerce logistics refers to the supply chain management process that delivers a product to a customer. Once a customer places an order via your online store, the logistics process picks, packs, and ships it to their home. It’s also known as “forward logistics” for this reason.
An efficient reverse logistics system handles moving inventory in the opposite direction. Customers expect to be able to return their items with no hassle and at little to no cost to them. It’s crucial to have a system in place to smoothly handle returns—one that doesn’t dissuade your customers from purchasing again.
The reverse logistics process
When a product makes its way back to your warehouse, reverse logistics processes looks something like this:

1. Customer initiates a return
The customer decides to ship a product back to the retailer. With a returns management system, the customer can print a returns label at home and either drop off the item at a pickup point or at a local store. The parcel will end up back at the retailer’s warehouse.
2. The product is inspected
Once the item arrives, it goes to a separate area of the warehouse for the retailer to decide what to do with the inventory. Incoming returns go through a review process where any sellable items are placed back on the shelf. Faulty or damaged items are put to one side to be recycled or refurbished.
3. The customer is refunded
The retailer decides whether the order meets your returns policy or refund criteria. Common criteria include the following:
-
Receiving the return within 14 days of the customer placing their order
-
Proof of purchase, such as a receipt or a digital record
-
Original packaging (including tags)
-
The product is unused or unworn
If this criteria is met, the retailer will refund the customer either through store credit or a direct refund to the credit card they paid on. Some brands take a cut out of this refund amount to cover the cost of return shipping.
4. The product is resold, refurbished, or recycled
Depending on the status of the product, the retailer has three options:
-
Reuse or resell it. If the product is still in great condition and looks as good as new, it can be resold to other customers. The retailer can either update their inventory counts or list the product on a resale or second-hand marketplace—like Allbirds does with its used shoes.
-
Refurbish it. If the product isn’t in resellable condition but could be with a few tweaks, the retailer could refurbish or remanufacture it and restart the product life cycle. For example, if a customer returned their phone case because it had cracked, you could apply a new layer of resin and resell it at a discounted price to a secondary market.
-
Recycle it. If the product is at its end-of-life or simply too costly to fix, the retailer can recycle or donate it. Brands that use proper disposal options (as opposed to landfill) can support the 32% of people who consider the environment all or most of the time when making purchases.
The benefits of a robust reverse logistics process
Ecommerce returns deserve the same attention as outgoing shipments. Let’s take a look at why an effective reverse logistics process is critical for ecommerce brands.

Cost savings
Storage space isn’t getting any cheaper. By 2024, retailers will be facing a 140-million-square-foot storage shortage, expected to increase the cost of warehousing.
Overcome that (and save your bottom line) with a streamlined reverse logistics process—one that is cost-effective and processes returns quickly and efficiently, resulting in faster inventory turnarounds.
Businesses spend around 20% to 30% of their total inventory value on carrying stock. Reverse logistics offers cost savings because it puts sellable items back on the shelf to be sold, while discarding others and freeing up storage space.
Increased customer satisfaction
Regardless of the direction of your inventory, customer loyalty is yours to win. The returns experience is just as important as the experience shoppers have when purchasing products through your online store.
Put yourself in the shoes of a customer. You’re left in the dark when returning an item; you don’t know when you’ll get your money back or if a replacement is on the way. That’s not a good customer experience.
But if you’re provided with updates at each point in the returns process and receive a refund quickly, you’re more likely to try another product from the same retailer. There’s no risk attached. Customers know that even if the second purchase they make eventually needs returning, the process is hassle free.
No wonder 96% of buyers that had an “easy” or “very easy” returns experience said they would shop with that retailer again.
Sustainability
These days, it’s not just price and quality that shoppers care about. Modern consumers want to know the brands they’re shopping with (and returning products to) are sustainable. In fact, two-thirds of consumers would pay more for products with environmentally sustainable practices or values.
Prove your commitment to sustainability through your reverse logistics operations. Jon Carder, co-founder and CEO of Vessel, says:
“Customers will participate in a company’s reverse logistics practices when they feel they’re doing something beneficial beyond themselves.
“One example is clothing retailer H&M. The chain collects used clothing in any condition at all their stores, and not just clothing that they’ve sold. The store uses the garments to create a clothing line made exclusively of used clothes. This system empowers people to get involved with a brand that prioritizes an eco-friendly way to sell clothing.”
Important data collected
Include a return form as part of your reverse logistics process for insight into your products. Analyze them to find areas for improvement—tweaks to make to your inventory that could limit the number of products being diverted back to your warehouse.
Pay close attention to:
-
Items with the highest return rates
-
Most popular reason for returns
-
Common faults or damages
Let’s put that into practice and say hair straighteners are your most returned item. Three-quarters of people who return the item do so because they didn’t realize the product only worked on wavy hair. Prevent this from happening—and your returns warehouse from being overrun with unsold inventory—by updating the product description on your website.
On the flip side, if you’re processing too many returns because the straighteners arrive damaged, fine-tune your reverse logistics process to quality control your inventory, invest in protective packaging, or choose a new shipping supplier.
Reverse logistics challenges
Investing in a reverse logistics program clearly has its benefits, but there are pitfalls to be aware of when planning your new process. Here are some of the biggest challenges when dealing with returns—and how to overcome them.
Customer expectations
There are only a certain number of hours in the day. And even with a large team powering your warehouse, processing returns and dealing with customer service queries is time consuming.
The blunt truth is: customers don’t care. They have strict expectations for the returns experience—and many won’t return to purchase from your store if you don’t hit the mark.
The biggest challenge for reverse logistics is the sheer amount of time it takes to process one return versus shipping out one order. It takes at least two to three times the amount of time. This challenge is exacerbated by labor shortages in our warehouse team.”
—Brian Lim, Founder and CEO of INTO THE AM
Solve this problem by clearly communicating your returns policy before the point of purchase. Explain when a refund is possible, the window of opportunity to return inventory, and how long customers should expect to wait for the return to be processed.
Quality control
Products involved in your reverse supply chain have been returned for a reason—be it that the customer ordered the wrong size or the item was faulty. A poor return logistics process leaves room for unsellable inventory to make its way back onto the shelf.
Prevent this from happening by establishing quality standards. Have your team test all returned inventory, not just those labeled as “wrong size” or “incorrect color” on the returns form. Does it still have the tags attached? Does it show obvious signs of use? Any product should be in pristine condition before restocking.
Do the same with any third-party logistics providers you’re working with to process returns. Share your quality standards with them and do random spot checks to make sure imperfect inventory is flagged.
It might seem like you’re throwing inventory away if it falls short of your quality standards, but remember the long-term impact on profitability. Reselling damaged inventory increases the likelihood of the same product being returned—and multiple returns of one item come with a price tag.
Lack of ownership
Who manages your reverse logistics process? Some retailers say their warehouse teams; others leave the responsibility with their operations manager. A handful simply say, “We’re not sure—it’s a mix of different roles.” Nobody to control the process means the responsibility (and therefore, your returns) are passed from pillar to post.
Establish a team to own your reverse logistics process. Scaling businesses could leave the responsibility to the inventory management team, while brands in the $10 million revenue range lend people from the supply chain team to manage reverse logistics management.
Without an owner, structure, processes, or comprehensive metrics, it is no surprise that companies have struggled to prioritize returns management.”
—McKinsey & Company
How to implement a reverse logistics process
There’s no way around it: a reverse logistic process needs to be enjoyable for everyone involved, no matter how many customer returns your business handles. There’s a lot at stake—customer satisfaction and loyalty included.
Here’s how to build a supply chain process that makes it quick and easy to handle returns, without falling short on customer expectations.
Choose a returns channel
The first step is to determine how a customer ships the product back to your warehouse. Options include:
-
Posting by mail. Should a customer want to exchange or refund the product, they can use a return label to post it back to the retailer. This option is preferred by 37% of customers.
-
Return to the store. If you have brick-and-mortar stores, allow shoppers who’ve bought items online to return it in their closest store.
-
Parcel pickup stations. Instead of pushing customers toward the post office, allow them to drop off their returns package at a nearby DHL Service Point or UPS Access Point.
From the retailer’s perspective, one channel reigns supreme: in-store drop off. Not only can processing returns in-store save time in the reverse logistics process, but driving customers in-store could reduce returns and increase revenue.
“More retailers are putting a heavier emphasis on ‘return to store’ as the more convenient option,” says Nikki Baird, VP of Retail Innovation at Aptos. “That doesn’t prevent returns, but it does make them cost less to the retailer.”
Customers who return items because they purchased the wrong size can easily get a replacement in-store, eliminating the need for returns altogether.
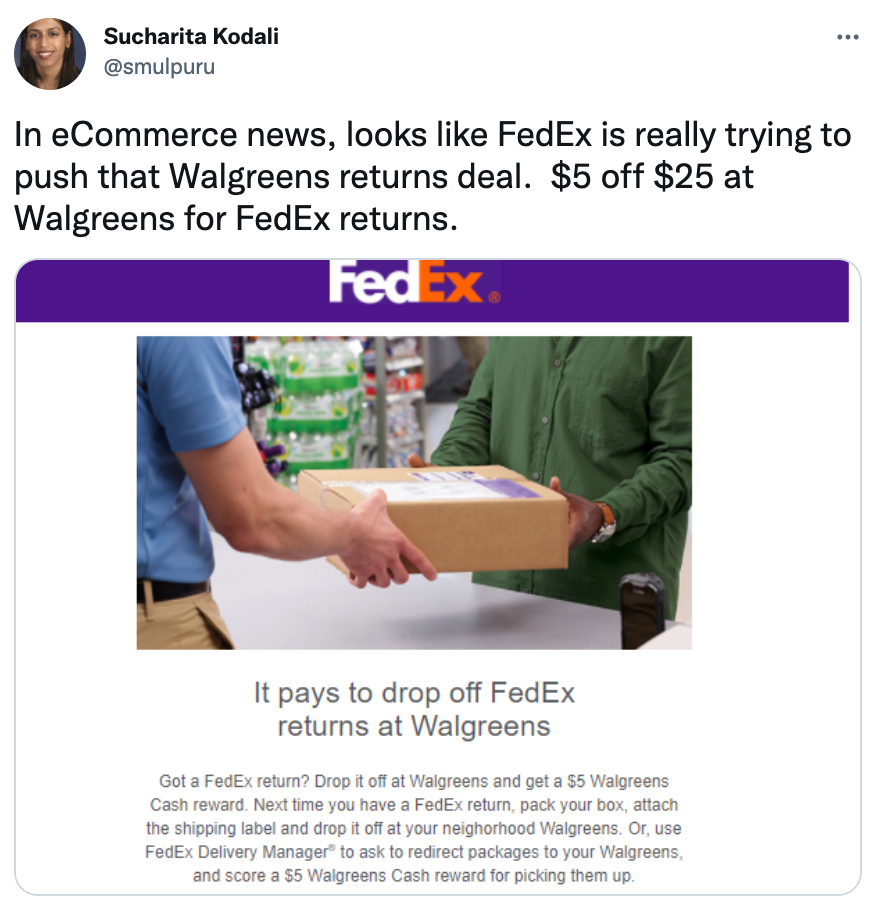
Plus, driving shoppers into your retail store gives you another opportunity to sell to them. Provide in-store experiences, engage browsers with friendly retail staff, and place low-cost items next to the checkout desk—all of which are techniques shown to improve retail conversion rates. It’s why brands like Walgreens are incentivizing shoppers to return FedEx items in-store.
Determine your return policy
There’s no way around it: a reverse logistic process needs to be enjoyable for everyone involved, no matter how many customer returns your business handles. There’s a lot at stake—customer satisfaction and loyalty included.
Here’s how to build a supply chain process that makes it quick and easy to handle returns, without falling short on customer expectations.
Choose a returns channel
The first step is to determine how a customer ships the product back to your warehouse. Options include:
-
Posting by mail. Should a customer want to exchange or refund the product, they can use a return label to post it back to the retailer. This option is preferred by 37% of customers.
-
Return to the store. If you have brick-and-mortar stores, allow shoppers who’ve bought items online to return it in their closest store.
-
Parcel pickup stations. Instead of pushing customers toward the post office, allow them to drop off their returns package at a nearby DHL Service Point or UPS Access Point.
From the retailer’s perspective, one channel reigns supreme: in-store drop off. Not only can processing returns in-store save time in the reverse logistics process, but driving customers in-store could reduce returns and increase revenue.
“More retailers are putting a heavier emphasis on ‘return to store’ as the more convenient option,” says Nikki Baird, VP of Retail Innovation at Aptos. “That doesn’t prevent returns, but it does make them cost less to the retailer.”
Customers who return items because they purchased the wrong size can easily get a replacement in-store, eliminating the need for returns altogether.
Plus, driving shoppers into your retail store gives you another opportunity to sell to them. Provide in-store experiences, engage browsers with friendly retail staff, and place low-cost items next to the checkout desk—all of which are techniques shown to improve retail conversion rates. It’s why brands like Walgreens are incentivizing shoppers to return FedEx items in-store.
Determine your return policy
A return policy explains the criteria an order (or product) needs to meet in order to qualify for a refund.
Not only can this minimize products being sent to the warehouse that you’re unable to refund, but you can also increase the conversion rate of your online store. Buyers look for a returns policy before making their first purchase.
Your return policy and procedures should outline:
-
Return window. How many days does a customer have to return their item?
-
What qualifies for a refund. Does the product need to be unused with tags? If the official returns window has passed, does it still need to be under warranty in order to qualify for a refund?
-
The type of refund on offer. Do you give store credit, exchange, or money back?
-
Who pays for return shipping. Many retailers bake the cost of returns into their product price. This builds good will with shoppers that feel waiving shipping fees on their next purchase will entice them to start shopping as soon as their refund has been processed.
Need help creating yours? Use Shopify’s free refund policy template, then upload it to the policies section of your store:
Have a designated space to handle returns
Once items make their way back to your warehouse, build a dedicated workspace for inventory to be processed and inspected.
“Sometimes returns can be messy and that can make you frustrated,” says Erin LaCkore, founder of LaCkore Couture. “To avoid that, make sure that your system is designed in such a way to divide returns into batches, separating them from the other incoming shipments.
“Develop a dedicated receiving process for returns. Distribution centers should have a separate workspace for the return shipments. They should have a proper process to handle the returns and also train their staff on what to do to properly process returns.”
Invest in return processing technology
Nobody wants a delay when getting their money back from a return. Keep customers on your good side—and increase the chances of them buying again—by investing in return processing technology.
Speed things up by investing in technology that helps you process returns faster, such as:
-
RFID scanners. Easily pinpoint the item being returned by scanning the barcode of a product. It’s especially useful if you’re processing large volumes of returns or have similar-looking SKUs.
-
Warehouse management software (WMS). Instead of recording returned inventory in an easily outdated spreadsheet, use a WMS. It’ll pull data from your RFID scanner and automatically update stock levels.
“Every single one of our items has an RFID tag in it, which is not like a GPS or something,” says Dean Jones, co-founder and CEO of GlamCorner. “It just allows clothing to move through at a phenomenal speed through all the different checkpoints all while keeping the customer informed. Has it left the warehouse? Has it returned back? Very important to our customer and for our team to be able to track where it is.”
Decide what to do with unsellable inventory
Earlier, we mentioned that quality control is a challenge for many companies. As part of your reverse logistics process, establish clear guidelines for when an item can be resold.
Decide what to do with anything that doesn’t hit the mark. Remember: The last thing you want is unsold goods cluttering your storage space, leaving less space for sellable inventory that generates revenue for the business.
Here’s what that might look like:
-
Items with small wear and tear marks are relisted at a discount
-
Faulty products are sent back to the manufacturer for refurbishment
-
Heavily damaged and unusable items are safely disposed of or recycled
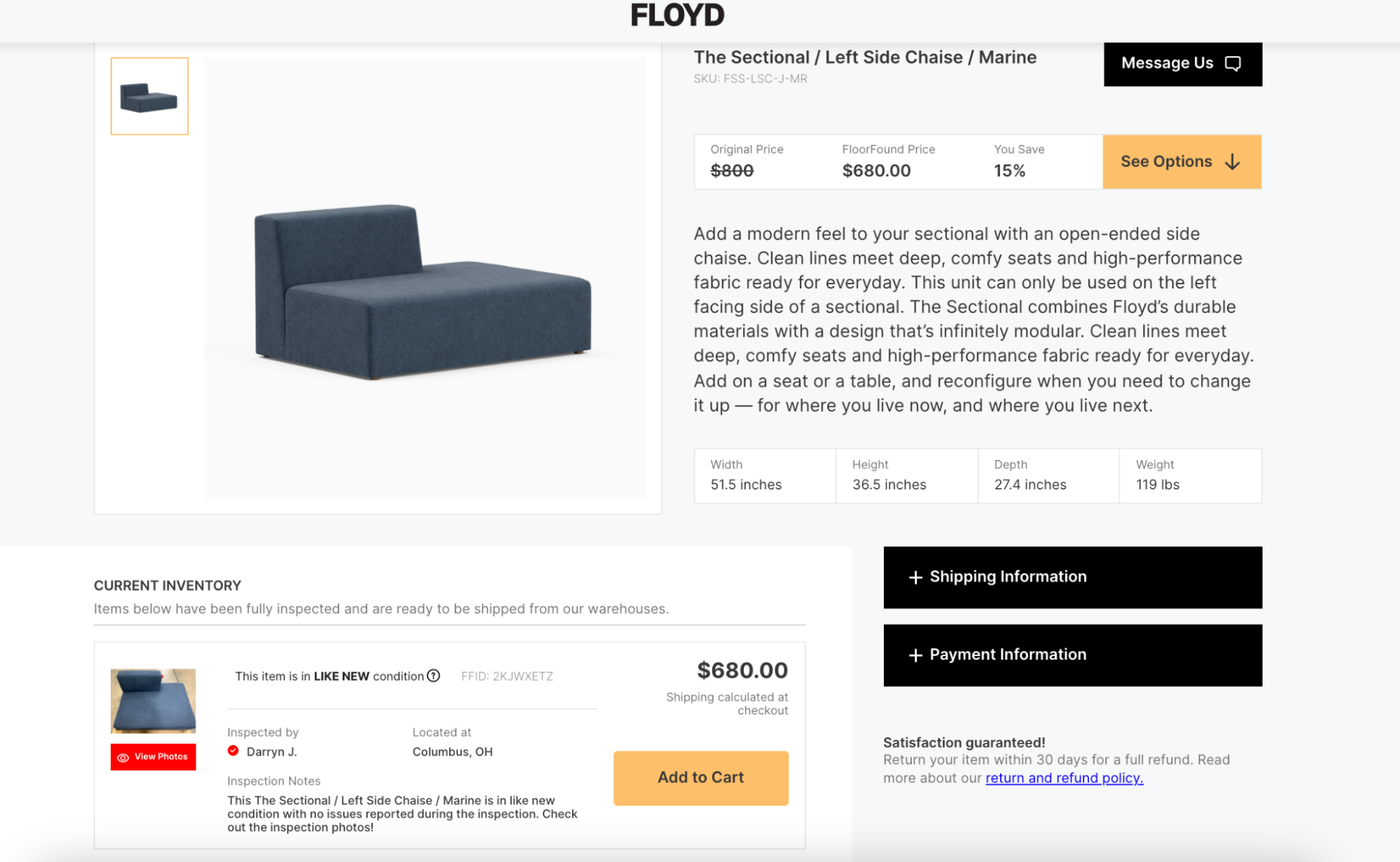
DTC furniture brand Floyd launched a resale marketplace to shift less-than-perfect inventory. The retailer collects unwanted items from a customer’s home and ships them back to the fulfillment center for quality inspection. Items are graded and relisted on the marketplace with a discount of between 15% and 50%.
Should I outsource reverse logistics?
Reverse logistics has many moving parts. While it’s possible to handle them internally, it might be time to consider outsourcing reverse logistics once you reach this point:
-
You’re receiving too many returns to manage them yourself
-
You’re finding it difficult to deal with or dispose of returned inventory
-
You don’t have the budget to invest in a reverse logistics team or dedicated technology
Shopify Fulfillment Network is built for scaling ecommerce businesses. They’ll store your inventory, and pick, pack, and ship orders across most of the United States within two days — freeing up your time so you can spend it on marketing, sales, customer support, and anything else that will help you grow.
The best part? Customers can ship returned products back to a Shopify fulfillment center. Their warehouse team will process the return and inspect the product, returning sellable inventory back to the shelf in preparation for future orders.
Shopify Fulfillment Network is always looking at what our business needs and incorporating those needs into their new services and features. As a business owner, fulfillment is only something you think about when it isn't working well and luckily I never have to think about it."
- Taylor Llewellyn, founder The Dad Hoodie
Need help with reverse logistics but don’t have the option to outsource it completely? Choose a shipping and returns app that integrates with your Shopify store, such as:
Ecommerce returns are inevitable
While there are steps you can take to prevent returns from overrunning your warehouse, ecommerce returns are an inevitable part of running a business.
Customer retention is at risk if your reverse logistics supply chain doesn’t meet expectations or maintain inventory quality, or if it’s too lengthy. So invest in return processing technology, outline your refund policy, and categorize inventory based on whether it can be resold.
Shopify Fulfillment Network exists to take those tasks off your plate. Outsource your reverse logistics so you can focus on what you do best.
Reverse Logistics FAQ
What is the meaning of reverse logistics?
Reverse logistics is the process of returning a product back to a retailer. The customer initiates their return and ships it back to the merchant’s warehouse. The item is then resold, refurbished, or resold.
What are the benefits of reverse logistics?
Merchants that optimize their reverse logistics process can retain more customers. If someone returns a product that is faulty, for example, a streamlined reverse logistics plan will refund them and send out a replacement before delays frustrate the customer.
What are the examples of reverse logistics?
-
Faulty items returned by a customer
-
Items returned by a wholesaler or retailer
-
Products that are refurbished
-
Items that are quality checked and resold
What are the 7 Rs of reverse logistics?
Receiving the product, reviewing it and repairing or refurbishing it to clear any defects. Items that aren’t reparable are refused, reused, or recycled.





